Cathodoluminescence (CL) Imaging for Defect & Material Characterization
Cathodoluminescence (CL) is a combination microscopy and spectroscopy technique that produces high-speed spectral maps of optical emissions with nanoscale resolution.
It is used to probe diverse features and properties of materials and devices, from the internal structures of direct bandgap semiconductors to surface plasmon resonances in metallic nanoparticles.
What is Cathodoluminescence (CL)?
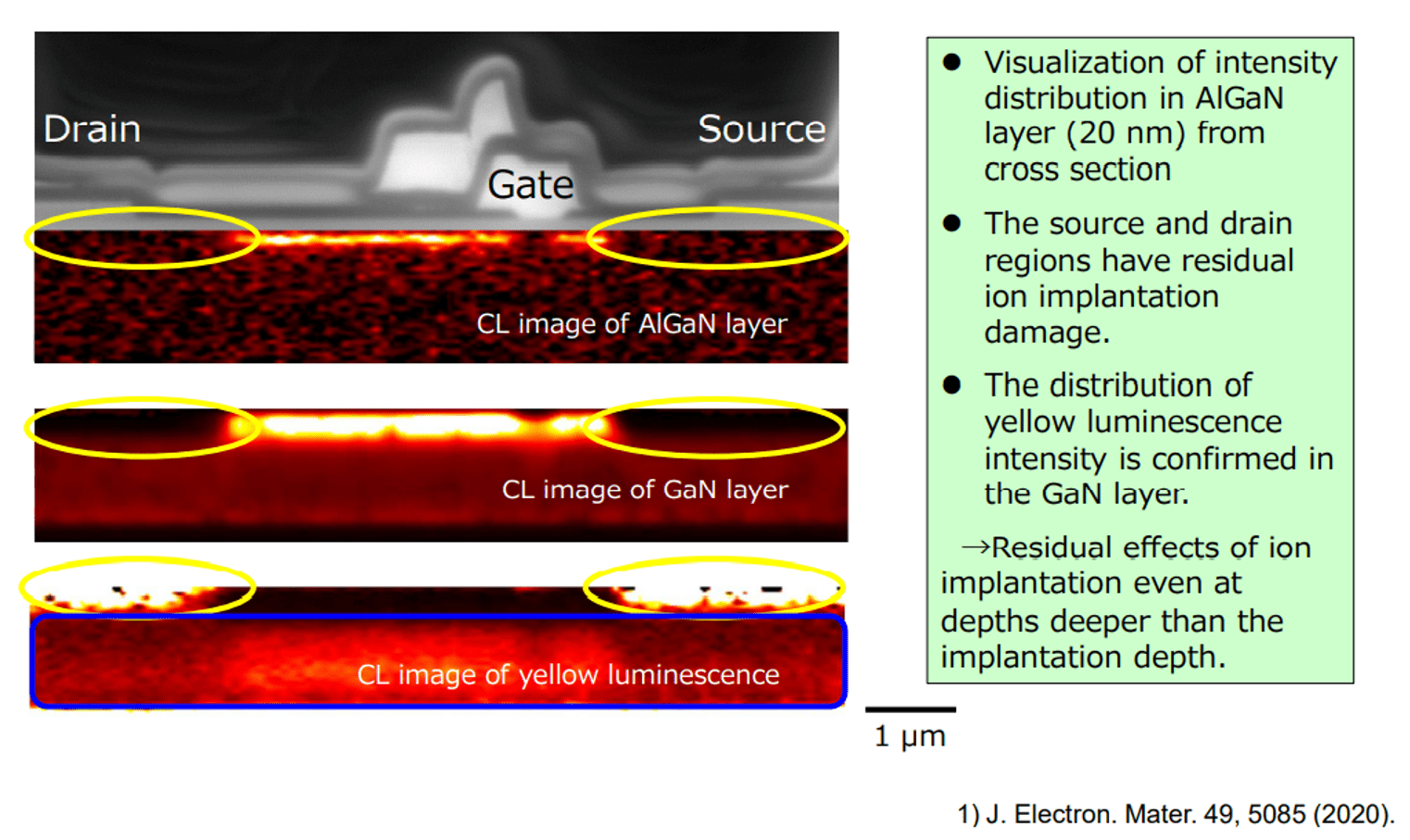
Cathodoluminescence (CL) is the emission of light from a material when it is bombarded by an electron beam, typically within a scanning electron microscope (SEM). This technique reveals critical information about a material’s band gap, crystallinity, defects, impurities, and carrier concentration, going beyond what standard elemental analysis provides.
CL offers high spatial resolution (up to 100 nm) and allows for 2D imaging of these properties across the sample. By adjusting the SEM’s accelerating voltage, the depth of analysis can be tuned. The method supports a broad spectral range from 200 to 1600 nm, and SEM images ensure precise targeting of the analysis area.
Our Process
Sample preparation
Use solid, vacuum-stable samples. Cross-sections or plan-view, depending on analysis needs.
Electron Beam Excitation
An electron beam hits the sample in an SEM, causing it to emit light.
Light Detection and Mapping
CL light is detected (200–1600 nm) to map defects, impurities, and band structure.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
High-resolution images and spectra reveal material quality and crystalline defects.
CL Instrument Used
- Wavelength Range: 200 – 1600 nm
- Acceleration Voltage: 0.5 – 30 kV
- Beam Current: up to 300 nA
- Measurement Area: 500 nm2 up to 1 mm2
- Temperature Range: Room Temp (~ 25 ⁰C)
- Cooling Unit can accommodate temperatures down to 30 K
- Cooling Unit can accommodate temperatures down to 30 K
- Cathodoluminescence Spectrometer is a Toray Original high-speed UV-Vis-NIR CL System based on HORIBA Jobin Yvon
-
- CCD
- Photomultiplier (visible and near-infrared EM radiation)
- InGaAs multi-channel detector
- Detectors

Strengths
- High speed spectral mapping
- High spatial resolution
- Wide wavelength range
- Suitable for in situ device analysis
- Specialized accessories accommodate cold experiments down to 30 K
Limitations
- Maximum area measured can be up to a millimeter scale
- Sample will receive some damage by the electron gun
- Organic materials are not ideal
Your Material Analysis Begins Here
Our team of experts is ready to provide a detailed and accurate quote tailored to your specific project requirements
Sample requirements
- Solid phase
- Vacuum stable
- Sample size limitations:
- 5-10 nm square analytical area
- Sample size 1 by 1 mm to 25 by 25 mm
- Maximum sample thickness: 3.5 mm or less
- Small chips can be analyzed by mounting on a dummy wafer
- Large wafers must be cut to size before analysis
